Browse Case Studies
By Industry
- Aviation
- Automobile
- Banking / Finance / Insurance
- Consumer Goods
- Education
- Electronics and Appliances Retail
- Media and Entertainment
- Food / Beverage
- Manufacturing
- Pharmaceuticals / Biotechnology / Health Care
- Retail
- Software
- Steel Industry
- Information Technology
- Transportation
- Telecommunications
- » All Industries
By Regions
Case Study Books
-
Corporate Governance
This casebook highlights how Corporate Governance (CG) has evolved and got importance after series of corporate scandals like Enron... -
Collaboration
Why should companies collaborate? When to collaborate? What precautions to be taken while venturing into a collaborative arrangement? - Case Study Books »
Executive Briefs
-
New Recruit MBAs Attitudes
Executive Brief with Lopamudra Ray, Keya Gupta, Deepika Lingala. -
Executive Brief on Power and Authority You Can’t Play by Rules, Always.
Executive Brief with Mr.R.D. Prasad, Product Manager. - Executive Brief»
Course Case Mapping For Marketing Management
While some business schools offer as one integrated and introductory course in Marketing, many other business schools split (taking into account the breadth and the depth of the body of knowledge) the course into two distinct modules - Marketing Management I and Marketing Management II. IBSCDC's marketing case studies have been mapped as per the latter approach - Marketing Management I & II. As everyone agrees, one of the ever green and increasingly demanding MBA subjects has been Marketing. The principles of marketing are being rewritten with extensive online market. Marketing Management I course case map is a well orchestrated blend of traditional marketing case studies and new age marketing case studies. Although each case study has been mapped for driving and deriving a specific concept, each of the case studies also presents an overlap of concepts. And at the discretion of the faculty, these case studies can accordingly be customized for respective audience.
Chapter : Introduction
Chapter : Introduction
Detailed Syllabus: Marketing – Definition of Marketing Management – Marketing Concepts – Evolution of Marketing – Marketing Mix, Marketing Challenges for the 21st CenturyKey Concepts: An Approach to Marketing Concepts
Case Study: Nano, Tata's People Car: Who is marketing?
Abstracts: Legendry marketing expert, the ‘Father of Modern Marketing’ Philip Kotler together with Theodore Levitt is accountable for defining the marketing concepts from traditional horse-trading habits of mid-20th century to modern marketing techniques. Marketing strategies pioneered during 1960s and 1970s led to fierce competition with dwindling profit margins due to increased market segmentation, commoditisation of products and shrinking product life cycles forcing manufacturers to make revolutionary new products to remain competitive in global markets.
The making of Tata Nano for a price of INR 1 lakh or $2000 portrays how an appropriate mix of marketing tools creates blockbuster products and sensation in consumer markets. The case delves into the marketing challenges in the Indian automobile industry and challenges posed during the manufacturing process of Nano. It proceeds to analyse how revolutionary products create buzz marketing and reduce the need of costs involved in product promotion.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 1, “Marketing in the Twenty-First Century”, Topic 1, “Marketing Tasks”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Marketing Myopia”, HBR, July-Aug 1960
- “Marketing is Everything”, HBR, Jan-Feb 1991
- “What Do Customers Really Want”, HBR, April 2009
- “Making The Perfect Marketer”, s+b
- “Proven Paths To New Markets Mastery”, Business Horizons, May-June 2002
- “Not Just Effective But Efficient: A New Blueprint for Marketing In An Era of Fragmented Media”, Booz, Allen & Hamilton
- “The Buzz On Buzz”, HBR, Nov-Dec 2000
- “Business Marketing: Understand What Customers Value”, HBR, Nov-Dec 1998
- “Economics Gift To Marketing”, Mercer Management
- An Interview with Martin Lindstrom
- An Interview with Richard Rawlinson
Case Study: Nestlé’s Marketing: The Next Driver of Value Growth?
Abstracts: Peter Brabeck, CEO of Nestle opined that marketing should be the backbone of the company to sustain growth in global markets. He integrated the marketing activities with strategic plans by repositioning the entire food group as a health corporation. The case study presents how Nestlé’s strategies were guided by principles of marketing innovation and an observation of balance between geographical activities and product lines.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 1, “Marketing in the Twenty-First Century”, Topic 3, “Company Orientation Toward the Market Place”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Corporate Imagination and Expeditionary Marketing”, HBR, Jul-Aug 1991
- “The Decline and Dispersion of Marketing Competence”, SMR, Summer 2005
- “The New Complete Marketer”, s+b
- “Results-Driven Marketing: A Guide to Growth and Profits”, s+b
- “A New Way To Market”, McKinsey Quarterly, 2000
- “Innovation versus Complexity: What Is Too Much of a Good Thing”, HBR, Nov 2005
Key Concepts: Marketing Mix
Case Study: Titan Industries: Getting the Marketing Mix Right
Abstracts: The case study highlights how companies that formulate appropriate marketing mix can succeed and become industry leaders. It delves into how Titan Industries engineered its marketing mix with sophisticated technology, innovative marketing, and high quality products to become a leading brand in the Indian Watch Industry.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 1, “Marketing in the Twenty-First Century”, Topic 2, “Marketing Concepts and Tools “, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Market Segmentation, Target Market Selection and Positioning”, HBS Note
- “Marketing Success Through Differentiation of Anything”, HBR, Jan-Feb 1980
- “New Criteria For Market Segmentation”, HBR, Mar-Apr 1964
- “The Role of Differentiation in Markets Driven By Advertising”, CMR, Spring 2003
- “Channel Champions: The Rise and Fall of Product-Based Differentiation”, s+b
- “Discovering New Points of Differentiation”, HBR, Jul-Aug 1997
- “Making Your Marketing Strategy Work”, HBR, Mar-Apr 1984
Key Concepts: Marketing Challenges in the New Millennium
Case Study: Ford’s Bumpy Market Share: A Marketing Makeover?
Abstracts: Referred as the ‘Industry of Industries” by Peter Drucker, US automobile industry’s so called ‘Big Three’ came under troubled waters in the new millennium due to intense foreign competition, eventually becoming the ‘Bankrupt Three’.
The case study focuses on the challenges faced by Ford Motors in the new millennium and how consumers value innovation, quality and services in the consumer markets. The ‘Big Three’ suffered from quality, reliability and safety related problems leading to loss of consumer faith and brand loyalty in the new millennium. Japanese automakers, in particular Toyota Motors posed a serious threat with its quality and fuel-efficient automobiles and lean manufacturing techniques forcing them to adjust their manufacturing and marketing strategies to sustain in the highly competitive marketing environment.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 1, “Marketing in the Twenty-First Century”, Topic 4, “How Business and Marketing Are Changing”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Market Share: A Key To Profitability”, HBR, Jan-Feb 1975
- “Strategies for High Market-Share Companies”, HBR, Nov-Dec 1975
- “Successful Share-Building Strategies”, HBR, Jan-Feb 1981
- “The Surprising Case For Low Market Share”, HBR, Nov-Dec 1982
- “Reality Is Perception: The Truth About Car Brands”, s+b
- “Driving Change: An Interview With Ford Motor Company’s Jacques Nasser”, HBR, Apr-May 1999
- “Marketing In Three Dimensions: The New Challenges for Marketers”, McKinsey&Co
Chapter : Micro Environment
Chapter : Micro Environment
Detailed Syllabus: The Company – Suppliers – Intermediaries – Customers – Competitors – PublicKey Concepts: Approach to Micro Management
Case Study: P&G: From Mass to Micromarketing
Abstracts: The case study analyses how the Cincinnati-based Procter and Gamble (P&G) a pioneer in mass marketing has revamped its marketing strategies in the new millennium from mass to micro marketing by understanding the core audience of its brands.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 3, “Winning Markets: Market-Oriented Strategic Planning”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Marketing Strategy: An Overview”, HBS Note
- “Marketing In An Age of Diversity”, HBR, Sep-Oct 1988
- “Pulling Away From Push Marketing”, HBR, May-Jun 1987
- “Globalization of Markets”, HBR, May-Jun 1983
- “Marketing Strategy Formulation”, HBS Note
- “Smart Customers, Dumb Companies”, HBR, Nov-Dec 2000
Key Concepts: Marketing Activities in the Micro Marketing Environment
Case Study: Corporate Communication: The Toyota Way
Abstracts: The case study provides insights into how Toyota executed marketing activities in a constellation of micro marketing environment. Its qualitative and creative corporate working environment that stimulates learning desire is the success factor of Toyota’s management style. Its corporate philanthropy encompassed eco-friendly activities, motor sport events such as Formula-One to reach out various segments of marketing environment.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 1, “Marketing in the Twenty-First Century”, Topic 2, “Marketing Concepts and Tools “, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- Chapter 3, “Winning Markets: Market-Oriented Strategic Planning”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Integrated Brand Communications”, Interbrand, Aug 2004
- “Integrated Marketing Communications”, HBS Note
- “The Role of Advertising in Brand Communications”
- “Marketing Communications Strategy”, London Centre of Marketing
Chapter : Macro Environment
Chapter : Supply and Demand Analysis
Detailed Syllabus: Demographic, Economic, Natural, Government Intervention in Natural Resource Management – Political Environment – Cultural EnvironmentKey Concepts: Effects of ‘Non- controllable Forces’ in Macro Marketing Environment
Case Study: Americanism, Brand America and American Brands
Abstracts: With the advent of globalisation during 1990s, renowned brands like Coca-Cola, Mc Donald’s, Microsoft, CNN, KFC and Marlboro etc penetrated into the global markets. American firms were viewed as a threat for local manufacturers and consumers in Europe and Asia resisted ‘Brand America’ and Americanism and viewed it as a threat to local manufacturers, consumers and their culture. The case study focused on how American brands like Coca-Cola and Mc Donald’s had attuned to the demographic, ethnic and cultural environments with appropriate marketing strategies.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 5, “Scanning the Marketing Environment”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Localizing in the Global Village: Local Firms Competing in Global Markets”, CMR, Summer 1999
- “Geopolitics and the Global Corporation”, s+b
- “How Global Brands Compete”, HBR, Sep 2004
- “Survival Strategies in a Hostile Environment”, HBR, Sep-Oct 1980
- “Navigating Five Currents of Globalization”, BCG (2005)
Chapter : Global Environment
Chapter : Global Environment
Detailed Syllabus: WTO- Basics for International Trade and Multi-national Investment – Operating in more than one national environment; Challenges Involved – Differences in Micro and Macro Environment: Bridging the International Gap.Key Concepts: Challenges Posed by MNCs while Operating in More than One National Environment
Case Study: Coca-Cola – Contentious Overseas Business Practices
Abstracts: Douglas Daft, CEO of Coca-cola believed in ‘Expanding from global to local’ and the companies business lay in the local markets, and the key success to the business growth was building relationships with suppliers, bottlers, transport companies, supermarkets and majorly with customers.
The case study was primarily written to understand how Coca-Cola faced controversial business allegations against its overseas business activities in Latin America, Europe, Uzbekistan, Middle-East and India posing serious challenges to its business activities.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 12, “Designing Global Market Offerings”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Globalization of Markets”, May-Jun 1983
- “Economic Evidence of the Globalization of Markets”, HBS Note
- “Global Strategy: In A World of Nations”, SMR, Fall 1989
- “All Strategy Is Local”, HBR, Sep 2005
- “Designing Global Strategies: Comparative and Competitive Value-Added Chains”, SMR, Summer 1985
- “Regional Strategies for Global Leadership”, HBR, Dec 2005
- “Distance Still Matters”, HBR, Sep 2001
- “Do You Really Have a Global Strategy”, HBR, Jul-Aug 1985
Chapter : Consumer Markets and Buyer Behaviour
Chapter : Consumer Markets and Buyer Behaviour
Detailed Syllabus: A Buyer Behavior perspective – Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior – Consumer Buying Roles – Types of Buying, Decision Behavior – The Buyer Decision Process – The Buyer Decision Process for New Products.Key Concepts: Consumer Behaviour
Case Study: Dell vs Lenevo: The Competitive Strategies in China
Abstracts: Having forayed into Chinese PC market in 1998, Dell Inc, primarily targeted Industrial and public service departments with its unique direct business model performing moderately well. As Chinese consumers exhibit a desire to touch and experience the products before making an actual purchase, Dell was faced with challenges to revamp its business model by establishing Kiosks to demonstrate and trial its products and features.
The case study delves into critical success factors of Chinese PC industry and the drawbacks in Dell’s marketing strategies to gain market foothold in Chinese PC markets.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 6, “Analysing Consumer Markets and Buyer Behavior”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Implicit Predictors of Consumer Behavior”, HBS Note
- “Foundations of Marketing Strategy: Product-Market Fit”, Richard Ivey School of Business Note
- “Inside the Mind of the Chinese Consumer”, HBR, March 2006
- “Marketing To China’s Consumers”, McKinsey Quarterly, 2004
- “Understanding The Chinese Consumer”, McKinsey Quarterly, 2004
- “Winning The Hearts and Minds of Chinese Consumers”, BCG Report, 2007
- “The Consumer Decision Journey”, McKinsey Quarterly, June 2009
Key Concepts: The Buyer Decision Process
Case Study: The Advent of the Internet and the Bargaining Power of the Customer
Abstracts: The advent of Internet brought sweeping changes in consumer buying process, shifting the focus from supplier of goods and services to the customer during late 20th century. The case presents how customers are empowered with modern tools of information search, evaluation of new alternatives and speeding up the buying process.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 6, “Analysing Consumer Markets and Buyer Behavior”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Contextual Marketing: The Real Business of the Internet”, HBR, Nov-Dec 2000
- “Driving E-Business Excellence”, SMR, Fall 2001
- “E-Commerce is Changing the Face of IT”, SMR, Fall 2001
- “The Emerging Model for Business In The Internet Era”, HBR, May-Jun 2000
- “How To Acquire Customers On The Web”, HBR, May-Jun 2000
- “The Future of Commerce”, HBR, Jan-Feb 2000
- “The Real Value of E-Business Models”, Business Horizons, Dec 2003
- “The Consumer Decision Journey”, McKinsey Quarterly, June 2009
- An Interview with Jeff Gee, www.ibscdc.org
Chapter : Industrial Markets
Chapter : Industrial Markets
Detailed Syllabus: Special Characteristics of Industrial Markets, Importance of Selling for an Industrial Marketer, Business Buying BehaviourKey Concepts: Challenges in Industrial Markets
Case Study: Indian Auto Components Industry
Abstracts: Indian Auto Component Industry during the recent years transformed from a low-key supplier serving the needs of domestic market to a supplier of high-value and critical automobile components provider to global automakers like General Motors, Toyota, Volkswagen and Ford and so on. The case study describes the characteristics and growth of Indian Auto components industry since liberalisation of markets in the Indian industrial context.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 7, “Analysing Business Markets and Business Buying Behavior”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Industrial Marketing Strategy: An Overview”, HBS Note
- “What is Industrial Marketing”, HBS Note
- “Industrial Selling: Beyond Price and Persistence”, HBR, Mar-Apr 1985
- “Post-Industrial Marketing”, HBR, Nov-Dec 1986
- “Trappings Vs Substance in Industrial Markets”, HBR, Jul-Aug 1970
Key Concepts: Business Buying Behaviour in Industrial Markets
Case Study: Semiconductor Industry: Samsung’s ‘BHAG’ or Bharat Forge: MNC in the Making
Abstracts: The need and application of Semiconductor ICs broadened with the proliferation of myriad consumer electronic products of present day world. They are the most vital components in manufacturing commercial products right from a small mobile phone to automobiles, military radars and weaponry system. Samsung ranked number two in manufacturing semiconductors with consistent performance in sales. The case study enables to understand the industrial buying behaviour in semi-conductor industry with rapid developments in personal computers, mobile telephones and telecommunications and automobile sectors.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 7, “Analysing Business Markets and Business Buying Behavior”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Segmenting Customers in Mature Industrial Markets”, HBS Note
- “How To Segment Industrial Markets”, HBR, May-Jun, 1984
Chapter : Segmenting and Targeting
Chapter : Segmenting and Targeting
Detailed Syllabus: Levels of Segmentation – Patterns of Segmentation – Procedures for Market Segmentation – Requirements of Effective Segmentation – Market Targeting – Evaluation & Selecting Target Markets, Focusing and Niching – Mass Customization.Key Concepts: Market Segmentation
Case Study: Indian Hotel Industry (A): The Competitive Dynamics
Abstracts: The case study highlights the market segmentation of Indian Hotel Industry after economic liberalisation of the country. Until recently India considered only five-star hotels as luxury and everything else as budget hotels, while the industry on global scale segmented as luxury, mid-scale, budget and economy hotels. The case explains the challenges faced by the Indian Hotel Industry due to high taxation, poor roads, limited tourism infrastructure, and bureaucratic visa processing system and so on.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 9, “Identifying Market Segments and Selecting Target Markets”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Market Segmentation, Target Market Selection and Positioning”, HBS Note
- “New Criteria for Market Segmentation”, HBR, Mar-Apr 1964
- “Smarter Segmentation For Your Sales force”, HBR, Mar 2004
- “Rediscovering Market Segmentation”, HBR, Feb 2006
- “Marketing Success Through Differentiation of Anything”, HBR, Jan-Feb 1980
- An Interview with P.Kiran, www.ibscdc.org
Key Concepts: Need of Market Targeting
Case Study: Sony Ericsson’s Alliance: The Synergies
Abstracts: Kazuo Nakai, Vice President Asia Pacific for Sony Ericson trusted until 2003 that company should have one hit model in each segment rather than having lot of undifferentiated ones. The case focuses on how Sony Ericson had initially focused on high-end low volume market, but realised later the need to foray into low-end high volume market targeting mass segments.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 9, “Identifying Market Segments and Selecting Target Markets”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Market Segmentation, Target Market Selection and Positioning”, HBS Note
- “Market Selection and Role of Product Portfolio Planning”, HBS Note
- “Driving an Operational Model That Integrates Customer Segmentation with Customer Management”, IBM Report
- “Targeting High-Value Customers: The Key To Profitability in Multichannel Retailing”, BCG Report
- “Rediscovering Market Segmentation”, HBR, Feb 2006
Chapter : Positioning
Chapter : Positioning
Detailed Syllabus: Competitive Differentiation – Concept of Positioning – Positioning as Strategy – Communicating your Positioning Strategy. Positioning by Usage, by User, by Product Benefit, etc.Key Concepts: Product positioning Strategies
Case Study: Toyota’s Scion (Guerrilla) Brand in US: The Marketing Positioning Strategies
Abstracts: Brian Bolain, a member of Toyota’s Genesis team suggested the need of changing the company’s strategies by positioning its new products targeting Generation Y customers. The case presents the dilemma of market positioning strategies of Toyota Scion in US focusing on to the taste of Gen Y customers.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 10, “Positioning the Market Offering Through the Product Life Cycle”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Stealth Marketing: How To Reach Customers Surreptitiously”, CMR, Summer 2004
- “Making Differentiation Make a Difference”, s+b
- “Analyzing Consumer Perceptions”, HBS Note
- “Ambush Marketing: A Threat To Corporate Sponsorship”, SMR, Fall 1996
- “Pulling Away From Push Marketing”, HBR, May-Jun 1987
Key Concepts: Communicating Product Positioning
Case Study: MTV In India: The Positioning Strategies
Abstracts: The case study presents how MTV focused on positioning its product offerings through various concepts like fashion, style, music, etc., to reach out the youth by way of various communication strategies like online, on ground and off-air activities.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 10, “Positioning the Market Offering Through the Product Life Cycle”, Topic 2, “Developing and Communicating a Positioning Strategy”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Avatar Based Marketing”, HBR, June 2006
- “Stealth Marketing: How To Reach Customers Surreptitiously”, CMR, Summer 2004
- “How To Reach The Young Consumer”, HBR, Mar-Apr 1974
- “Marketing To Generation”, HBR, June 2003
Key Concepts: Positioning by User Segments
Case Study: Madura Garment’s New Product Mix and Positioning Strategies Big Battle for Small Clothes
Abstracts: Ever since Madura Garments forayed into Indian Textile markets it offered famous brands like Allen Solly, Van Hussein, Louis Philippe and Peter England catering to the apparel needs of various user segments. The case highlights how Madura Garments explored new market segments stretching its brand offerings from men’s wear to women’s wear to kid’s apparels.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 10, “Positioning the Market Offering Through the Product Life Cycle”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Where Babies Come From: Supply and Demand in an Infant Market Place”, HBR, Feb 2006
- “Proven Strategies for New Market Mastery”, Business Horizons, 2002
Chapter : Building Customer Satisfaction
Chapter : Building Customer Satisfaction
Detailed Syllabus: Through Quality, Service and Value – Defining Customer Value and Satisfaction – Delivering Customer Value and Satisfaction – Retaining Customers – CRMKey Concepts: Customer Satisfaction
Case Study: Dell’s Dilemma: Corporates or Consumers?
Abstracts: The case highlights how Dell’s direct business model benefited both the company and customers with its customised products providing a competitive advantage to the company. It simplified the process of product search, geographic location, average unit price, and total dollar value, thus ensuring optimum customer satisfaction by establishing a 1-1 two-way contact.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 2, “Building Customer Satisfaction, Value and Retention”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Business Marketing: Understand What Customers Value”, HBR, Nov-Dec 1998
- “Building Loyalty In Business Markets”, HBR, Sep 2005
- “Customer Intimacy and other Value Disciplines”, HBR, Jan-Feb 2003
Key Concepts: Value-Chain Analysis
Case Study: Dell in India Targeting SMB Markets: The Differentiation strategies
Abstracts: The case study focuses on value chain analysis of Dell’s direct business model of selling and build-to-order supply chain philosophy that ensures the supply of products directly from supplier to customers establishing a two-contact for feed back and ensuring that the company maximizes the profits and customers derive satisfaction.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 2, “Building Customer Satisfaction, Value and Retention”, Topic 3, “Delivering Customer Value and Satisfaction”,Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Building Loyalty In Business Markets”, HBR, Sep 2005
- “Business Marketing: Understand What Customers Value”, HBR, Nov-Dec 1998
- “Customer Value Propositions in Business Markets”, HBR, Mar 2006
- “Five Rules for Winning Emerging Market Consumers”, A T Kearney
- “Winning The Indian Consumer”, McKinsey Quarterly, 2005
- “The New Indian Consumer”, HBR, Oct 2006
Key Concepts: Understanding Relationship Marketing
Case Study: Customer Relationship Management at Harrah’s Entertainment
Abstracts: Michael Porter introduced a new marketing concept called ‘Competitive Advantage’ and defined it as an advantage that a company can enjoy over its competitors position. This advantage can be achieved when it ensures greater customer satisfaction either by lowering prices or providing extended benefits and services to offset the prices. The case study delves into how Harrah’s successfully managed competitive advantage by ensuring customer relationship with the help of science and IT and analysing the behavioural patterns of its customers.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 2, “Building Customer Satisfaction, Value and Retention”, Topic 4, “Attracting and Retaining Customers”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Building Customer Relationships That Last”, HBR, Nov-Dec 1985
- “CRM: Profiting From Understanding Customer Needs”, Business Horizons, Sep-Oct 2004
- “CRM Done Right”, HBR, Nov 2004
- “How To Delight Your Customers”, CMR, Fall 2005
- “The Microeconomics of Customer Relations”, SMR, Winter 2006
- An Interview with Don Peppers and Martha Rogers, www.ibscdc.org
Chapter : Product Decisions
Chapter : Product Decisions
Detailed Syllabus: Product Classifications – Individual Product Decision Product-mix Decisions – Product-line DecisionsKey Concepts: Modular Approach in Production
Case Study: IKEA in Japan: The Market Re-entry Strategies
Abstracts: The case study presents the modular production strategies of IKEA’s low-cost furniture with a slogan ‘one-size fits all’ in Japanese furniture markets. It debates the reasons for its failure during its first entry in 1974 and the factors that encouraged re-entering the Japanese market with the ensuing challenges.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 13, “Managing Product Lines and Brands”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Market Entry Strategies: Pioneers Vs Late Arrivals”, s+b
- “Beating The Odds in Market Entry”, McKinsey Quarterly, 2005
Chapter : Developing New Products
Chapter : Developing New Products
Detailed Syllabus: New Product Development Processes – Challenges in Developing New Products – Consumer Adoption Process for New Products.Key Concepts: New Product Development
Case Study: P&G’s ‘Design Thinking’ Initiative: The Innovation Lessons
Abstracts: The case study highlights P&G approach of new product development with open-business model by connecting consumer wants and company’s innovation technology. The case explains P&G’s innovative learning methods and its understanding about customer habits, wants and behaviour.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 11, “Developing New Products”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Managing New Product Development Process”, HBS Note
- “The New Product Imperative”, HBS Note
- “Why Consumers Don’t Buy: The Psychology of New Product Adoption”, HBS Note
- “Connect & Develop: Inside P&G’s New Model for Innovation”, HBR, March 2006
- “The New Product Development Map”, HBR, May-Jun 1989
- “From The Ladder of Science to the Product Development Cycle”, HBR, Nov-Dec 1989
- “Co-opting Customer Competence”, HBR, Jan-Feb 2000
- “The Co-creation Connection”, s+b
Key Concepts: Customer Adoption Process
Case Study: Apple’s iPod: Product Development and Extension Strategies
Abstracts: Philip Kotler remarked the success of iPod was the combination of its excellent product design, smart marketing and great timing. Apple’s timed launch with smart marketing strategies made customers more willing to adopt to the MP3 concept that ensured a superior product concept.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 11, “Developing New Products”, Topic 4, “The Consumer-Adoption Process”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Extend Profits, Not Product Lines”, HBR, Sep-Oct 1994
- “The Future of New Product Development”, McKinsey Quarterly, 2003
- “The Logic of Product Line Extensions”, HBR, Nov-Dec 1994
- “When Product Variety Backfires”, HBS Working Knowledge
Chapter : Life Cycle Strategies
Chapter : Life Cycle Strategies
Detailed Syllabus: Product Life-cycle – Stages in PLC – Brand Life Cycle – Marketing StrategyKey Concepts: Product Life Cycle Strategies
Case Study: Lifebuoy in India: The Product Life Cycle Strategies
Abstracts: The case study enables in understanding the behaviour of Lifebuoy’s product life cycle during various stages of its life and the strategies it adopted by repositioning and rejuvenating the brand with a new life cycle.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 10, “Positioning the Market Offering Through the Product Life Cycle”, Topic 4, “Product Life-Cycle Marketing Strategies”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Exploit The Product Life Cycle”, HBR, Nov-Dec 1965
- “Forget The Product Life Cycle Concept”, HBR, Jan-Feb 1976
- “Product Life Cycle”, HBS Note
- “Break Free From The Product Life Cycle”, HBR, May 2005
Case Study: Hyundai “Santro” in India: Product Life Cycle Strategies
Abstracts: JI Kim, managing director of Hyundai Motors was quite happy with the overwhelming success of Santro’s market performance and remarked that the company has been assiduously focusing on delivering not cars but joy and happiness. The company made its debut with its ‘Santro’ in India in 1998. Santro was positioned in premium compact car segment and priced less than its nearest rival Maruti Zen. The case study highlights the product life cycle strategies of Santro by offering new variants in the category with models like Santro Zip Drive, Santro Zip Plus, and Santro Xing to prolong its growth stage.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 10, “Positioning the Market Offering Through the Product Life Cycle”, Topic 4, “Product Life-Cycle Marketing Strategies”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Market Analysis”, HBS Note
- “Link Manufacturing Process and Product Life Cycles”, HBR, Jan-Feb 1979
- “The Dynamics of Process-Product Life Cycles”, HBR, Mar-Apr 1979
- “Beware The Product Death Cycle”, s+b
Key Concepts: Brand Life Cycle
Case Study: Brand Bond: The World is Not Enough
Abstracts: Ian Fleming’s fictional character James Bond excelled for four decades by changing its product offerings periodically to suit the contemporary demand of markets without changing the core value. The case demonstrates the long mileage of the brand image in tune with the changing customer preferences and technological revolutions in the film industry.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 10, “Positioning the Market Offering Through the Product Life Cycle”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “The Brand Ultimatum”, MM
- “Managing Brands For The Long Run: Brand Reinforcement and Revitalization Strategies”, CMR, Spring 1999
- An Interview with Al Ries, www.ibscdc.org
Chapter : Marketing of Services
Chapter : Marketing of Services
Detailed Syllabus: Basic Concepts and Issues – Nature and Characteristics of Service – Marketing Strategies for Service Firms – International Services Marketing – Person, Place and Idea Marketing, Strategies throughout PLCKey Concepts: Strategies of Services Marketing
Case Study: IndiOne: The Indian ‘Premium’ Hotel for the ‘Bottom of the Pyramid’
Abstracts: The case provides insights into how Tata Group’s ‘IndiOne’, a no-frill model hotel, created landmark innovation in Indian Hotel industry with simple and smart basics like simplicity, convenience, informality, warmth, modernity and affordability in the industry.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 14, “Designing and Managing Services”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Exploit Your Product’s Service Life Cycle”, HBR, Sep-Oct 1988
- “Putting The Service-Profit Chain to Work”, HBR, Mar-Apr 1994
- “Production Line Approach To Service”, HBR, Sep-Oct 1972
- “Strategy Is Different In Service Businesses”, HBR, Jul-Aug 1978
- “The Four Things a Service Business Must Get Right”, HBR, Apr 2008
- “Making Better Investments at the Bottom of the Pyramid”, HBR, May 2009
- “Serving the World’s Poor, Profitably”, HBR, Sep 2002
- An Interview with P. Kiran, www.ibscdc.org
- An Interview with Aneel Karnanin, www.ibscdc.org
- An Interview with Reuben Abraham, www.ibscdc.org
- An Interview with Dr. Miguel Angel Gardetti, www.ibscdc.org
- An Interview with Vivekanandan, www.ibscdc.org
Chapter : Distribution and Channel Decisions
Chapter : Distribution and Channel Decisions
Detailed Syllabus: Nature of Distribution Channels – Channel Design and Modification Decisions – Physical Distribution and Distribution Cost Analysis, Channels – The Middlemen – The Wholesaler – Retailing – Evolution, Types of Retailing – Telemarketing, Retailing – The Supplier Market – The Multi-channel System – The Super Market – Mail-order – Transportation – Warehousing – Inventory ManagementKey Concepts: Channels of Distribution
Case Study: Dell’s Direct Model: Change of Direction?
Abstracts: Despite being a late entrant in the PC industry, Dell Inc., snatched the No.1 spot from HP in 2003 with its direct distribution model and build-to-order approach. The case study presents how Dell’s direct distribution model became the envy of PC manufacturers and made it a darling on Wall Street by virtually integrating itself by building close relationships with suppliers and customers. The case also debates whether it missed out the opportunities in successfully responding to the changing environments in US PC markets.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 16, “Managing Marketing Channels”, and Chapter 17, “Managing Retailing, Wholesaling and Market Logistics”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “How Dell Got Soul”, s+b
- “The Power of Virtual Integration: An Interview with Michael Dell”, HBR, Mar-Apr 1998
- “Customer-Driven Distribution Systems”, HBR, Jul-Aug 1987
- “Seven Rules of International Distribution”, HBR, Nov-Dec 2000
- An Interview with Dr. Dr. Bolko V Oetinger, www.ibscdc.org
Key Concepts: Supply-chain Management
Case Study: P&G’s Logistics Revolution Co-creating Value
Abstracts: The case study highlights P&G’s philosophy of Customer Driven Supply Network and ability to win customers with two critical ‘moments of truth’ after purchase process. It explores the manufacturer-retailer relationships in co-creating value and identifying supply-chain as a profit centre rather than a cost centre, a source of competitive advantage in ensuring top-line growth as well as bottom-line performance.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 16, “Managing Marketing Channels”, and Chapter 17, “Managing Retailing, Wholesaling and Market Logistics”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Creating Value Through Supply Chain Management”, A T Kearney
- “Strategic Sourcing: From Periphery to the Core”, HBR, Feb 2005
- “How To Do Strategic Supply Chain Planning”, SMR, Fall 2003
- “Logistics: Essential To Strategy”, HBR, Nov-Dec 1977
Key Concepts: Designing a Channel System for Marketing Products and Services
Case Study: Organized Retailing in India: Opportunities and Challenges
Abstracts: The evolution of organised retailing after liberalisation changed the conventional supply-chain channel model that was designed in such a way that a producer was directly selling the goods to the customers during shopping seasons. The case delves into how organised retailing set its feet with the rise in income levels of affluent middle class in India since 1990s and the evolution of super markets and shopping malls that adopted scientific supply-chain channel system.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 16, “Managing Marketing Channels”, and Chapter 17, “Managing Retailing, Wholesaling and Market Logistics”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Indian Retail: On The Fast Track”, KPMG
- “Retailing in India: Getting Organized to Deliver Growth”, A T Kearney
- “The Bird of Gold: The Rise of India’s Consumer Market”, McKinsey Global Report
- “Window of Hope for Global Retailers”, A T Kearney 2009 GRDI
Key Concepts: Modifying the Channel Arrangement in Marketing Environment
Case Study: Wal-Mart’s Foray into Japan: Heading towards Success or Hara-Kiri?
Abstracts: The case study presents Wal-Mart’s reentry into Japan with modified supplier-retailer relationship strategies in the Japanese retail industry. It was faced with challenges like Japan’s multi-tier distribution system, understanding Japanese buying behavior and creating a right product assortment to remain competitive in the industry.
- Background Reading/ Additional Reading:
- Chapter 16, “Managing Marketing Channels”, and Chapter 17, “Managing Retailing, Wholesaling and Market Logistics”, Marketing Management, Philip Kotler, The Millennium Edition
- “Retailing Industry”, HBS Note
- “Beating The Odds in Market Entry”, McKinsey Quarterly, 2005
- “Gateways to Entry”, HBR, Sep-Oct 1982
- “Tracking The Elusive Consumer”, s+b
- “Understanding The Customer Experience”, HBR, Feb 2007

- What products/services are we selling and how do they fit into the ‘needs-requirement’ itinerary of the customers? What is the life of these products/services? (marketing concepts, products/services, needs hierarchy, PLC strategies)
- What is the geographical reach of these products/services and how does the environment affect the ‘reach’ decisions? (micro, macro and global environment; consumer markets; industrial markets)
- Who are the “relevant” customers for these products/services/How to identify the ‘relevant’ customers for this product category? (segmentation, targeting)
- What is the ‘relevant customers’ buying behavior? What factors influence their buying behavior?
- What’s the best way to reach these ‘relevant’ customers? How to ‘position’ our products/services in their minds? (Distribution channels; positioning)
- How do we attract them to buy our products/services? How do we ensure that we continue to have their loyalty? (Building customer satisfaction ; developing new products)
This Course Seeks to Address the Following Questions
The purpose of a business is to create customers it can serve profitably. A business fulfills this purpose by providing a product or service that satisfies a customer need. The satisfaction of this need provides value to customers for which they are willing to pay. The customers’ perceived importance of this need determines how highly they value the product or service and what they are willing to pay for it. Effective marketing is viewing the company from the outside, from the customers’ perspective. Customers buy solutions to problems and businesses sell products or services that provide these solutions. The essence of marketing is linking customers’ problems to business products and services.
Why Marketing Management - I for an MBA?
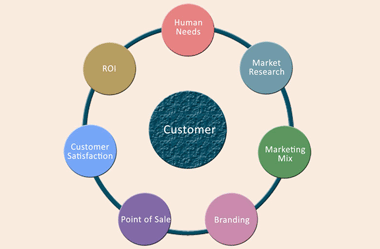
Value offered means nothing without communicating that value to a potential customer. And how do you do that?
Marketing
Everything a company does is marketing-related. From how you answer the phone, to what is printed on your invoices, to how engineering thinks about design, to how the CFO establishes and communicates financial policy, everything should be evaulated on the basis of whether or not it improves the companies ability to get and keep a customer. The point of Drucker’s comment is that without a customer, there is no business. Without thoughtful product/service development, there is no value to communicate. Winning the hearts of customers is the job of marketers. Do that and their wallets will follow.
- “Pepsi to Apple: An Odyssey”, John Sculley
- “The Real Thing – Truth and the Power at Coca-Cola Company”, Constance L. Hays
- “Rising Tide : Lessons from 165 Years of Brand Building at Procter & Gamble”, Davis Dyer, Frederick Dalzell and Rowena Olegario
- “Sneaker Wars”, Barbara Smit
- “Why We Buy – The Science of Shopping”, Paco Underhill
- “The Art of War (Sun Tzu)”, James C. Clavell
- “Marketing As Strategy: Understanding the CEO’s Agenda for Driving Growth and Innovation” Nirmalya Kumar (3 Vs: valued customer (who to serve), value proposition (what to offer) and value network (how to deliver).
- Direct from Dell: Strategies that Revolutionized an Industry – Michael Dell, Catherine Fredman
- 22 Immutable Laws of Marketing – Al Ries & Jack Trout
Widely Used Books for Marketing Management
- The Hudsucker Proxy
The movie is an aweinspiring creation of a goofy, dumb hero having ‘greatness thrust upon him’. It is a theme plotted on corporate corruption and the mind set of those who are responsible for organisational development and growth. Norville Barnes (Tim Robbins) was appointed as the proxy president of Hudsucker industries by Machiavellian executive Sidney J. Mussberger (Paul Newman), who intends to forestall a public takeover company by lowering investor confidence, thereby driving down the price of shares and allowing the board to purchase the controlling asset.
- Tucker: The Man and His Dream
Preston Tucker, an American automobile designer had a dream of producing a classic Tucker car of his times that other contemporary cars could not design with features like an air-cooled rear engine, disc brakes, independent 4-wheel suspension, and additional center head light that could be pivoted left and right for better vision when turning. Although he could succeed raising money, create product demand and set up a factory, unfortunately unlike many small entrepreneurs he too failed to fight the big guys in the industry and failed to fulfill his dreams. Tucker’s failure to fulfill his Big, Hairy, Audacious Goal defines the success and failure of entrepreneurs and entry-level barriers in industries despite capable of developing revolutionary new products.
- Salesman
Paul Brennan, an Irish-American and his colleagues, a group of real-life Bible salesmen for the Mid-American Bible Company traipses door-to-door in an effort to sell the book to housewives who find it hard to afford but don’t want to appear rude to a Church-sanctioned representative. The documentary was a collaboration of Maysles brothers that tells how Brennan exchanges war-time stories with fellow Bible-sellers and attends management and sales meetings.
- The Corporation
The movie was a well-orchestrated and fascinating documentary about the growing significance of global businesses, and the impacts of corporate decision process to the external world. It highlights how corporates have ballooned in size and power since industrial revolution and how the loopholes in laws enabled managers to remain unaccountable for their actions. It examines the corporate behaviour, history, culture, environment, and deliberate attempts to break laws to reap benefits.
- Super Size Me
The movie is a great documentary about the manufacturing processes of a billion-dollar fast food industry besieged by doctors, lawyers and nutritionists. It reflected how fast food industry exploited poor Americans by satisfying their materialistic appetites and becoming a self-seeking money machine at the cost of Americans health. It highlights the harmful effects of school lunch programs, declining health and physical education standards, food addictions and tough measures people adopt to lose weight to gain their health.
- Thank You for Smoking
Aaron Eckhart plays Nick Naylor, a lobbyist for the Cigarette industry who travels, talks, spins arguments over their heads to ensure that people keep on smoking. The movie is plotted on a political drama and a funny social satire of the first rank. It highlights how tobacco industry in US wields political power because of its ability to saturate political process with money. According to Centre for Responsive Politics tobacco industry gave more than $7 million dollars to President Bush and republicans during 2000 elections and $1.4 million to democratic during the same period. The story is plotted around tobacco industry’s efforts to prevent Senator Ortolan K.Finistirre’s from nailing them from peddling addictive and unhealthy products.
- Will Success Spoil Rock Hunter?
A comic satire of 1950s television in which a writer for advertising, Rockwell P. Hunter (Tony Randall), desperately puts all his efforts to convince a beautiful movie star Rita Marlow to endorse for product promotion. After the successful endorsement of the model, his commercials rock the market and he moved up the ladder at work becoming company president, but his triumph in the world of advertising cost him to loose his fiancée.
- An Inconvenient Truth
The movie is focused on a critical issue like global warming intended to deliver as a wake-up call to the world. Al Gore, the lead role in the film takes the issue to the road after he failed presidential bid to raise awareness and inspire people on the crisis levels of green house gases and the havoc they are wreaking on the planet.
- Fahrenheit 451
Oskar Werner plays the role of Montag, a fireman whose mission was to burn all books and collections on sight. His duty was to burn the books at a temperature of 450 degrees F because government believes that books make people unhappy and fears they create independentthinking public. He never questions what he does or why he does until he meets a lady Clarisse when he begins to read confiscated books and suspects the motives of government behind book-burning.
- Cast Away
Tom Hanks the Federal Express Executive was stranded in a deserted island as his plane crashes on a fight over South Pacific. The film progresses with Hanks attempts to survive using the remnants of plane’s material and his eventual escape to join the civilization. Hanks abilities to preserve and hope are a product of his life-changing experiences. The film provides an understanding in greater detail how product placement functions in individual films and affects the narrative and texture of a film. The movie included product placement of two prominent brands Wilson Sporting Goods and Fed-Ex. Though the idea of Fed Ex plane crash was not liked by the company, it was convinced later due to its brand awareness in Asia, Europe and other parts of the world.
Hollywood Classics
- “Exploit The Product Life Cycle”, HBR, 1965
- “Forget The Product Life Cycle Concept”, HBR, January–February 1976
- “Link Manufacturing Process and Product Life Cycles”, January–February 1979
- “Dynamics of Process Product Life Cycles”, HBR, March–April 1979
- “Break Free From The Product Cycle”, HBR, May 2005
- Theodore Levitt, “Marketing Myopia”, HBR, July –August
- “Marketing is Everything”, HBR, January–February 1991
- “Basic Quantitative Analysis for Marketing”, HBS Note, September 1986
- “Borden’s Hierogliphics Marketing Strategy”, Darden’s Note
- “Competitive Positioning”, HBS Note, September 1994
- “Market Segmentation, Target Market Selection and Positioning”, HBS Module Note, April 2006
- “New Criteria For Market Segmentation”, HBR, March–April 1964
- “Discovering New Points of Differentiation”, HBR, July–August 1997
- “Marketing Success through Differentiation”, HBR, January–February 1980
- “Ending the War Between Sales and Marketing”, HBR, July–August 2006
- “Marketing Strategy – An Overview”, HBS Note, March 2003
- “Analyzing Consumer Perceptions” HBS Note, December 2001
- “Market Selection and Direction: Role of Product Portfolio Planning”, HBS Note, November 1984
- “From Segments to Target Segments”, Book Chapter from Marketing as Strategy
- “Economics Gift to Marketing”, Mercer Management Consulting, 2003
- "Pulling Away from Push Marketing", HBR, March–Junuary 1987
- “Can Marketing and Manufacturing Co-Exist”, HBR, September–October 1977
- “Good Product Support is Smart Marketing”, HBR, November–December 1983
- “Creating Value”, HBR, October 2000
- “Eager Sellers and Stony Buyers”, HBR, Junuary 2006
- “Why Consumers Don’t Buy? The Psychology of New Product Adoption”, HBR, April 2004
- Gadiesh Orit and Gilbert L. James, “Profit Pools: A Fresh Look At Strategy”, HBR, May–June 1998
- “The Sales Learning Curve”, HBR, July–August 2006
- “Avatar-Based Marketing”, HBR, June 2006
- “Masterly Marketing”, HBR OnPoint Collection
- “Making The Perfect Marketer”, s+b
Must-read Article Inventory
| Individual Case Material for a Course (assuming 40 students) |
Course Case Pack (CCP) | |
| Case Studies | 40 X Rs.200 X 31 cases = Rs.248000 |
|
| Structured Assignments | 40 X Rs.150 X 20 SAs = Rs.120000 | |
| Teaching Notes | 20 X Rs.400 = Rs.8000 | |
| TOTAL | Rs.376000 ($7520) | Rs.50000 ($1000) |
| Per Student | Rs.9400 ($188) | Rs.1250 ($25) |
Buy This Case Pack
-
Course Pack contains
- 31 Case studies
- 20 Structured Assignments
- 20 Teaching Notes
Related Links
Executive Interviews
- George Wright
Speaks on Decision Making - Michael Beer
Speaks on Change Management - Michael Roberto
Speaks on Change Management - Gary David
Speaks on Multicultural Teams - Michael Hammer
Speaks on Change Management - Executive Interviews »
Video Interviews
- Mir Ranjan Negi
Speaks on Managing Troubled Times - Viren Wilfred Rasquinha
Speaks on Executive Education & Sports Managment in India - Edward Cohen
Speaks on Managing Organizational Trauma - Video Interviews»